
The Air Quality Hazards of Ozone Pollution in Indoor Air
15 December 2022
The indoor environment has more air quality hazards than just Covid-19 particles themselves. According to the WHO, air pollution is the world’s greatest environmental health threat. Many people have always believed that ozone in the air is a double-edged sword . It has the side of sterilizing and inactivating viruses, but also has the side of endangering human health. Modern research suggests that ozone in indoor air is now one of the most significant pollutants to human health.
Ozone is one of the strongest chemical oxidants known
Ozone is a colorless gas with a special fishy smell. Ozone decomposes slowly at room temperature. Ozone is one of the strongest chemical oxidants known and it plays an important role in air pollution. Under the action of ultraviolet rays, ozone reacts photochemically with hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides to form photochemical smog with a strong stimulating effect.
Health hazards of ozone pollution
In the lower troposphere of the atmosphere, ozone is also contained, but its concentration is much lower than that of the stratosphere. In unpolluted air, the concentration of ozone in the lower atmosphere is generally ( 0.005-0.05) × 10-6. At this concentration, ozone is harmless. Contrary to the beneficial ozone in the upper stratosphere, low-altitude ozone is a harmful gas with a pungent odor and a biocidal effect.
The harm of ozone to the human body mainly has the following effects:
- When the concentration of ozone in the low-altitude atmosphere reaches (0.1~0.5) × 10-6, it will irritate the respiratory tract, causing sore throat, chest tightness cough, asthma attack, and can stimulate the trachea and cause bronchitis. When the ozone concentration is higher, it may cause sternal pain, decreased lung permeability, emphysema, pulmonary edema, and exacerbate respiratory diseases.
- Cause neurotoxicity, leading to symptoms such as dizziness, headache, vision loss and memory loss. Excessive exposure to high-concentration ozone can also damage the central nervous system and lead to thinking disorders.
- Destroys the immune function of the human body and reduces the disease resistance of the human body. Ozone may also induce chromosomal aberrations in lymphocytes, impair enzyme activity, affect thyroid function, and cause early calcification of bones. Long-term excessive inhalation of ozone will affect the metabolism of cells in the body, reduce the resistance of the lungs to bacteria, and accelerate human aging.
- Ozone can also destroy vitamin E in human skin, causing skin wrinkles, dark spots and other skin diseases.
What is even more unexpected is that in recent years, American scientists have also pointed out that ozone can affect the quantity and quality of men’s semen, thereby affecting fertility. Studies have also pointed out that long-term excessive inhalation of ozone by pregnant women may cause baby deformities.
It should be worth noting that not only industrial waste gas brings high concentration of ozone on the ground, but also some common equipment, especially things found in the office. Most of the printers and copiers we use frequently work on the principle of static electricity, and may also produce ozone and some organic waste gases. Long-term exposure may cause cardiovascular diseases and even cancer.
Ozone is highly oxidizing, and ozonated air is corrosive to almost all metals except gold and platinum. Aluminum, zinc, lead will be strongly oxidized when in contact with ozone. Ozone also has a strong corrosive and destructive effect on non-metallic materials.
When the concentration of ozone in the air reaches ( 0.05~0.15) × 10-6, it will have different harmful effects on many plants. Tobacco, spinach, oats, etc. are all plants sensitive to ozone, and damage will occur in 0.5 to 8 hours in such air. Potatoes, barley, beans, onions, wheat, tomatoes, etc. are also very sensitive to ozone. In the absence of symptoms, plant growth can also be markedly stunted. Ozone can also destroy the ability of plants to absorb carbon dioxide and aggravate the greenhouse effect. High concentrations of ozone can also reduce the growth of plants, leading to a decline in crop yields.
Ozone can reach the deep part of the respiratory tract, and has a strong stimulating effect on the respiratory organs, causing the contraction of the respiratory tract. The degree of its stimulation is better than that of nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide, and its toxicity to the respiratory system is more than 10 times greater than that of nitrogen oxides. The olfactory threshold of ozone is very low. When the concentration reaches 0.02 ppm, you can smell the odor; At 1ppm, the eyes, nose, and throat are dry, with burning sensation, and headache. No matter how long the time is, the central nervous system will be disturbed and the thinking will be disordered. In addition, ozone can also hinder the function of blood oxygen transport, resulting in tissue hypoxia; damage to thyroid function, bone calcification, and potential systemic effects, such as inducing lymphocyte chromosomal aberration, damaging the activity of certain enzymes and producing hemolytic reactions .
6,000 non-smokers in the United States have shown that there exists a relationship between ozone exposure and the incidence of lung cancer. At the same time, there are reports that ozone can trigger asthma. Cumulative exposure is an important factor, and long-term low-level exposure can have health effects.
Long-term exposure to ozone can lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, COPD). According to a report, in 2017, long-term ozone exposure alone caused 472,000 deaths from COPD worldwide, of which China accounted for 38% (178,200 people). The number of deaths caused by ozone exposure has been increasing in recent years. Global deaths from ozone exposure increased by 4% from 1990 to 2010; from 2010 to 2017, deaths increased by about 15%.
Asthma disease burden caused by short-term exposure to ozone pollution higher than PM 2.5
Short-term exposure to ozone can exacerbate asthma and cause other respiratory diseases. The research team of Professor Anenberg of George Washington University evaluated the disease burden caused by short-term exposure to ozone and found that about 9-23 million asthma emergency cases worldwide may be caused by short-term exposure to ozone, even higher than short-term exposure to PM2.5’s. The disease burden of asthma makes up 5-10 million visits per year. Excessive ozone in the air will have a significant impact on human health. It can cause breathing problems, trigger asthma, reduce lung function and trigger lung disease. In Europe, ozone is currently one of the air pollutants of greatest concern. Several European research reports have pointed out that for every 10µg/m3 increase in ozone exposure concentration, the daily mortality rate will increase by 0.3%, and at the same time, the heart disease mortality rate will also increase by 0.4%. Recent findings have shown a robust correlation between daily mortality and ozone levels when ozone concentrations are below 120µg/m3. Accordingly, the previously proposed 8-hour average limit of 120 µg/m3 was reduced to 100 µg/m3.
The oil on human skin reacts with ozone to produce dangerous pollutants
An interdisciplinary collaboration of atmospheric chemists and engineers in Germany, Denmark, France, and the United States has shown that oils on human skin react with ozone to generate powerful free radicals that can further react with most organic compounds in the indoor environment, thereby Produces hazardous pollutants.
A study published in the journal Science details this reaction pathway, which helps explain how the body directly affects the chemical composition of indoor environments. It could also help research into the detrimental health effects of inhaling toxic compounds, which we produce in part, experts say.
“People are aware of pollution outside, but when they go inside they think, ‘Oh, now we’re safe.’ That’s not true,” said study co-author Jonathan Williams, of the Cyprus Institute and Max Planck of Germany. Atmospheric chemist at the Gram Institute of Chemistry. “It was a surprising finding that ozone reacts on our skin and releases more chemicals into the air around us.”
The source of ozone in the air
Ozone in indoor air mainly comes from the atmosphere. The normal atmosphere contains a very small amount of ozone, the concentration is about 0.02 mg/m 3 ~0.06mg/m 3 , with an average of 0.03mg/m 3 . While sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides in air polluted cities produce photochemical smog, the concentration of ozone generated will exceed the background value of the atmosphere by several times or even ten times. The maximum allowable concentration in natural air is 0.1mg/m 3 .
According to the 2019 Global Air Quality Report, the quarterly population-weighted ozone concentrations of the 11 most populous countries in the world range from 45 to 68 ppb, which is about 0.09 to 0.136 mg/m 3 . Compared with PM 2.5, the regional differences in ozone concentration are small on a global scale, so whether it is a developed country or a developing country, ozone pollution is one of the great challenges facing the prevention and control of air pollution.
Unlike the ozone layer in the upper atmosphere, ground-level ozone is the main component of photochemical smog. It is produced when pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) from vehicles and industry and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from vehicles, solvents and industry react with sunlight (photochemical reactions). Ozone pollution is at its worst when the weather is sunny.
Low-concentration ozone does not meet the requirements for disinfection
Ozone can directly interact with bacteria and viruses, destroying their cells and ribonucleic acid, and decompose macromolecular polymers such as DNA, RNA, lipids, and polysaccharides. However, to meet the requirements of air disinfection, the concentration of ozone is dozens of times higher than the health limit standard.
The air in a confined space is treated with ozone at a concentration of 5~10mg/m3 for 30 minutes to meet the requirements of air disinfection. Low-concentration ozone cannot meet the qualified requirements for disinfection.
The health limit standard for ozone in indoor air is 0.1mg/m 3 . It can be seen that the allowable ozone concentration in the air is far from the disinfection standard, and low concentrations of ozone are harmful and not beneficial.
US UL standard puts forward zero ozone requirements for air purifiers

UL is the abbreviation of Underwriter Laboratories Inc. UL Safety Testing Institute is the most authoritative institution in the United States and is also the institution engaged in safety testing and appraisal in the world. UL certification is an independent, for-profit professional organization that conducts tests for public safety. After nearly a hundred years of development, UL has become a world-renowned certification body.
In 2019, the US UL standard put forward zero ozone requirements for air purifiers.
Ozone safety testing of air purifiers
How does an air purifier perform ozone safety testing?
EU mandatory standard EN 60335-2-65, 101 The ozone concentration produced by air-cleaning appliances shall not be excessive.
Compliance is checked by the following test, which is carried out in a room without openings having dimensions of 2,5 m x 3,5 m x 3,0 m, the walls being covered with polyethylene sheet. If the instructions state that the appliance is to be fixed in a room having a volume exceeding 30 m3, the dimensions of the test room are increased accordingly.
The appliance is positioned in accordance with the instructions. Appliances used on a table are placed in the centre of the room approximately 750 mm above the floor.
The room is maintained at approximately 25 °C and 50 % relative humidity. The appliance is supplied at rated voltage for 24 h, removable filters being removed if this is more unfavourable.
The ozone sampling tube is to be located in the air stream 50 mm from the air outlet of the appliance. The background ozone concentration measured prior to the test is subtracted from the maximum concentration measured during the test.
The percentage of ozone in the room shall not exceed 5 x 10-6.
Air Purifiers for Ozone Removal
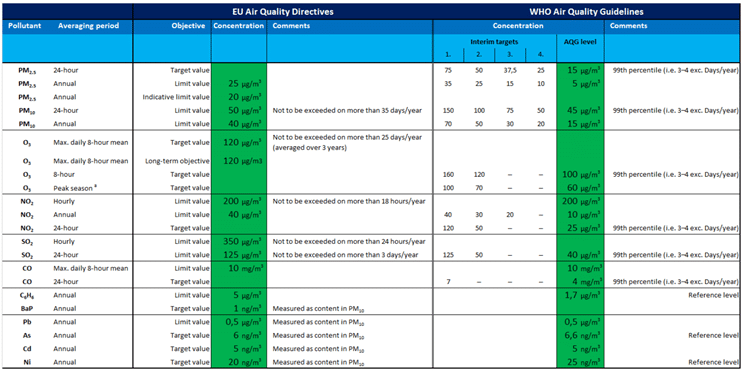
The Evidence Assessment of the Health Effects of Air Pollution is a project within the framework of the 2013 WHO -led review of EU policies to tackle air pollution. The project aims to develop evidence-based responses that address issues related to the importance of air quality management, while addressing specific issues for certain air pollutants. To this end, WHO established a dedicated scientific advisory board to guide the global academic experts involved in the project. The 2005 WHO Air Quality Guidelines are intended to provide global guidance for reducing the health impacts of air pollution. However, while the original Code applied only to the European Union, the latest version in 2005 was compiled based on an expert assessment of current scientific evidence and applies globally. The latest guidelines recommend setting limits for the concentrations of the following air pollutants, including respirable particulate matter (PM), ozone (O3), nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and sulfur dioxide (SO2). EU Environment Commissioner Janez Potočnik announced that the 2013 policy to tackle air pollution will be the focus of EU policy. The plan aims to draw attention to the importance of clean air and implement actions to improve air quality across the EU. The burden of disease caused by short-term exposure to indoor ozone, and the health benefits of reduced ozone concentrations.
Latest News

Oxford based air purification experts Healthy Air Technology Ltd recognised at CIBSE Building Performance Awards
News release: Oxford based air purification experts Healthy Air Technology Ltd recognised at CIBSE Building Performance Awards The…

Cloud seeding and air pollution
Recent poor air quality in regions such as Pakistan, China and the UAE has led to the use…

Are scented candles dangerous to indoor air quality?
Recent news articles questioning if scented candles are dangerous to indoor air quality have helped to highlight the…

